|
|
| Line 57: |
Line 57: |
| <!-- Examples must be written with the Example template. --> | | <!-- Examples must be written with the Example template. --> |
| {{Example|Lawyer Calibration | | {{Example|Lawyer Calibration |
| |[[File:Credence Level Lawyers.png|thumb|Lawyer calibration curve.]]
| | |[[File:Credence Level Lawyers.png|thumb|Lawyer calibration curve.]] |
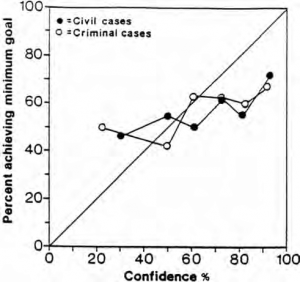
| Lawyers have a wide range of predictions (20%-100%) for how likely they are to win any given case. However, the actual results show a much narrower band (40%-70%). Really, the outcome is more of a toss-up. [[:File:Insightful or Wishful- Lawyers' Ability to Predice Case Outcomes - Delahunty, Granhag, Hartwig, Loftus.pdf|(Source)]]
| | Lawyers have a wide range of predictions (20%-100%) for how likely they are to win any given case. However, the actual results show a much narrower band (40%-70%). Really, the outcome is more of a toss-up. [[:File:Insightful or Wishful- Lawyers' Ability to Predice Case Outcomes - Delahunty, Granhag, Hartwig, Loftus.pdf|(Source)]] |
| }} | | }} |
| {{Example|Nurse Calibration | | {{Example|Nurse Calibration |
| |[[File:Credence Level Nurses.png|thumb|Nurse calibration curve.]]
| | |[[File:Credence Level Nurses.png|thumb|Nurse calibration curve.]] |
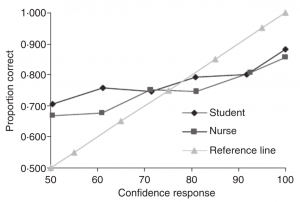
| Calibration curves are shown for experienced nurses as well as students training to become nurses. In both cases, they appear to be overconfident when outcomes are more likely and underconfident when outcomes are less likely. The nurses did not seem to become better calibrated with time. [[:File:Nurses' Risk Assessment Judgements; A Confidence Calibration Study - Yang, Thompson.pdf|(Source)]]
| | Calibration curves are shown for experienced nurses as well as students training to become nurses. In both cases, they appear to be overconfident when outcomes are more likely and underconfident when outcomes are less likely. The nurses did not seem to become better calibrated with time. [[:File:Nurses' Risk Assessment Judgements; A Confidence Calibration Study - Yang, Thompson.pdf|(Source)]] |
| |comments={{BoxCaution|title=Note|The confidence values are all greater than 50%. Any prediction whose confidence is less than 50% can be rephrased as a prediction for the opposite with a confidence greater than 50%. (e.g. I'm 30% confident it will rain tomorrow means I think it will ''not'' rain tomorrow with 70% confidence.)}}
| | |comments={{BoxCaution|title=Note|The confidence values are all greater than 50%. Any prediction whose confidence is less than 50% can be rephrased as a prediction for the opposite with a confidence greater than 50%. (e.g. I'm 30% confident it will rain tomorrow means I think it will ''not'' rain tomorrow with 70% confidence.)}} |
| }} | | }} |
| {{Example|Weather Forecaster Calibration | | {{Example|Weather Forecaster Calibration |
| |It is possible (and expected) for singular election forecasts to turn out to be wrong some of the time. It is fine as long as the predictions within that credence range are overall well calibrated. It is also impossible to calibrate the credence of a singular prediction, it is only possible for an aggregate of predictions. [[:File:The Polls Weren't Great. But That's Pretty Normal. - Silver.pdf|(Source)]]
| | |It is possible (and expected) for singular election forecasts to turn out to be wrong some of the time. It is fine as long as the predictions within that credence range are overall well calibrated. It is also impossible to calibrate the credence of a singular prediction, it is only possible for an aggregate of predictions. [[:File:The Polls Weren't Great. But That's Pretty Normal. - Silver.pdf|(Source)]] |
| }} | | }} |
| {{Example|Vague Verbiage and Words of Estimative Probability | | {{Example|Vague Verbiage and Words of Estimative Probability |
| |Words of estimative probability are vague terms used by intelligence analysts to convey the likelihood of an event without explicitly stating the associated probability.
| | |Words of estimative probability are vague terms used by intelligence analysts to convey the likelihood of an event without explicitly stating the associated probability. |
| |links={{LinkCard
| | |links={{LinkCard |
| |url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Words_of_estimative_probability | | |url=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Words_of_estimative_probability |
| |title=Words of Estimative Probability | | |title=Words of Estimative Probability |